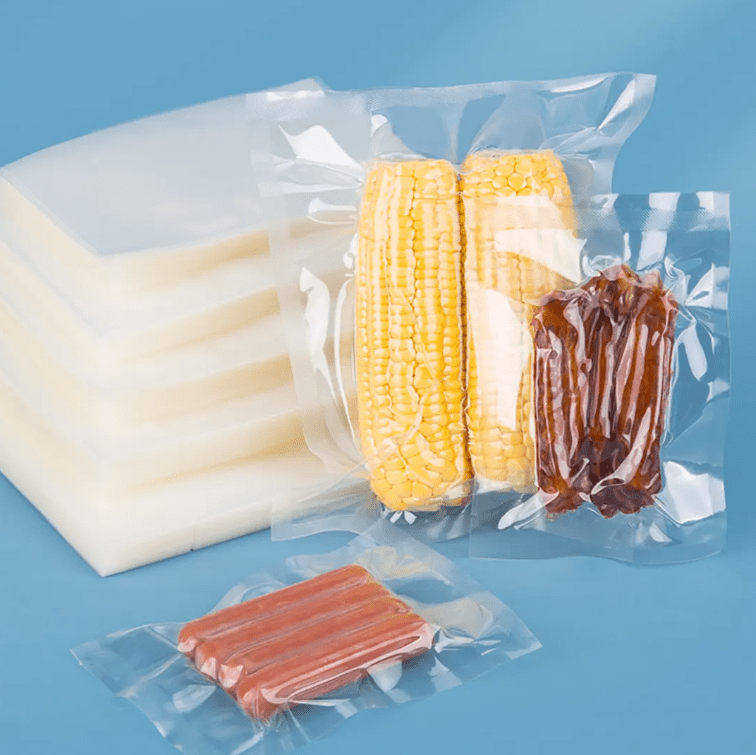
A vacuum bag is a flexible container designed to be emptied of air to create a vacuum seal. Here is a detailed introduction:
Structure and Material

- Structure: It typically consists of a bag – like body with a sealing mechanism, such as a zipper – like closure or a heat – sealable edge. Some vacuum bags may also have a valve or opening through which the air is removed.
- Material: Vacuum bags are usually made of plastic materials, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or a combination of both. These materials are chosen for their flexibility, durability, and ability to withstand the pressure difference when vacuum – sealed. Additionally, some bags may have a layer of aluminum or other barrier materials to enhance their resistance to moisture, oxygen, and light.
Working Principle

The working principle of a vacuum bag is based on the removal of air from the bag. When the air is sucked out, the pressure inside the bag decreases, creating a vacuum. The external atmospheric pressure then presses against the bag, tightly compressing the contents inside. This helps to achieve several purposes, such as reducing the volume of the stored items, protecting them from dust, moisture, and oxidation, and preventing the growth of mold and bacteria.
Applications

- Household Use: Vacuum bags are widely used for storing clothes, bedding, pillows, and other textile items. By removing the air, they can significantly reduce the space occupied by these items, making it easier to store them in closets, under beds, or in storage boxes. They are also useful for protecting seasonal clothes from dust and pests when not in use.
- Food Storage: In the food industry, vacuum bags are used to package and preserve food. Vacuum – sealing food helps to extend its shelf life by reducing the amount of oxygen available, which slows down the growth of microorganisms and the oxidation process. This is particularly important for perishable foods such as meat, fish, cheese, and baked goods. Vacuum – sealed food bags also help to prevent freezer burn when storing food in the freezer.
- Industrial Applications: Vacuum bags find applications in various industrial processes. For example, in the electronics industry, they are used to package sensitive electronic components to protect them from electrostatic discharge and moisture. In the automotive industry, vacuum bags may be used to store and transport parts that need to be protected from corrosion and damage. They are also used in the medical field to package sterile medical supplies and equipment.
Advantages

- Space – Saving: The most obvious advantage is the significant reduction in volume achieved by compressing the contents. This is especially beneficial for storing bulky items in a limited space.
- Protection: Vacuum – sealing provides an effective barrier against external factors such as dust, moisture, oxygen, and pests. This helps to keep the stored items in good condition for a longer period, protecting them from damage, spoilage, and deterioration.
- Convenience: Vacuum bags are easy to use. Most bags have a simple sealing mechanism that allows for easy opening and closing. They are also lightweight and portable, making it convenient to move and store the items.
Disadvantages

- Limited Reusability: While some vacuum bags can be reused, the sealing mechanism may wear out over time, reducing the effectiveness of the vacuum seal. Additionally, if the bag is punctured or damaged, it will no longer be able to maintain a vacuum.
- Not Suitable for All Items: Some items may not be suitable for vacuum – sealing. For example, items that are prone to crushing or deforming, such as delicate fabrics with intricate designs or certain types of electronics, may be damaged by the pressure of the vacuum bag.